


The asynchronous behavior led to the formation of a wide range of meiotic products. mass of DNA in single Aedes aegypti cell in prophase II a) 1.5 pg.
Consequently, the scattered chromosomes produced telophase II nuclei of different sizes in situ. 2)At what part of the cell cycle would you see a chromosome that looks like this. Cells with non-aligned chromosomes in the metaphase II plate did not receive the "go ahead" sign to initiate anaphase II. Meiosis II is similar to a normal Mitosis.
Prophase ii full#
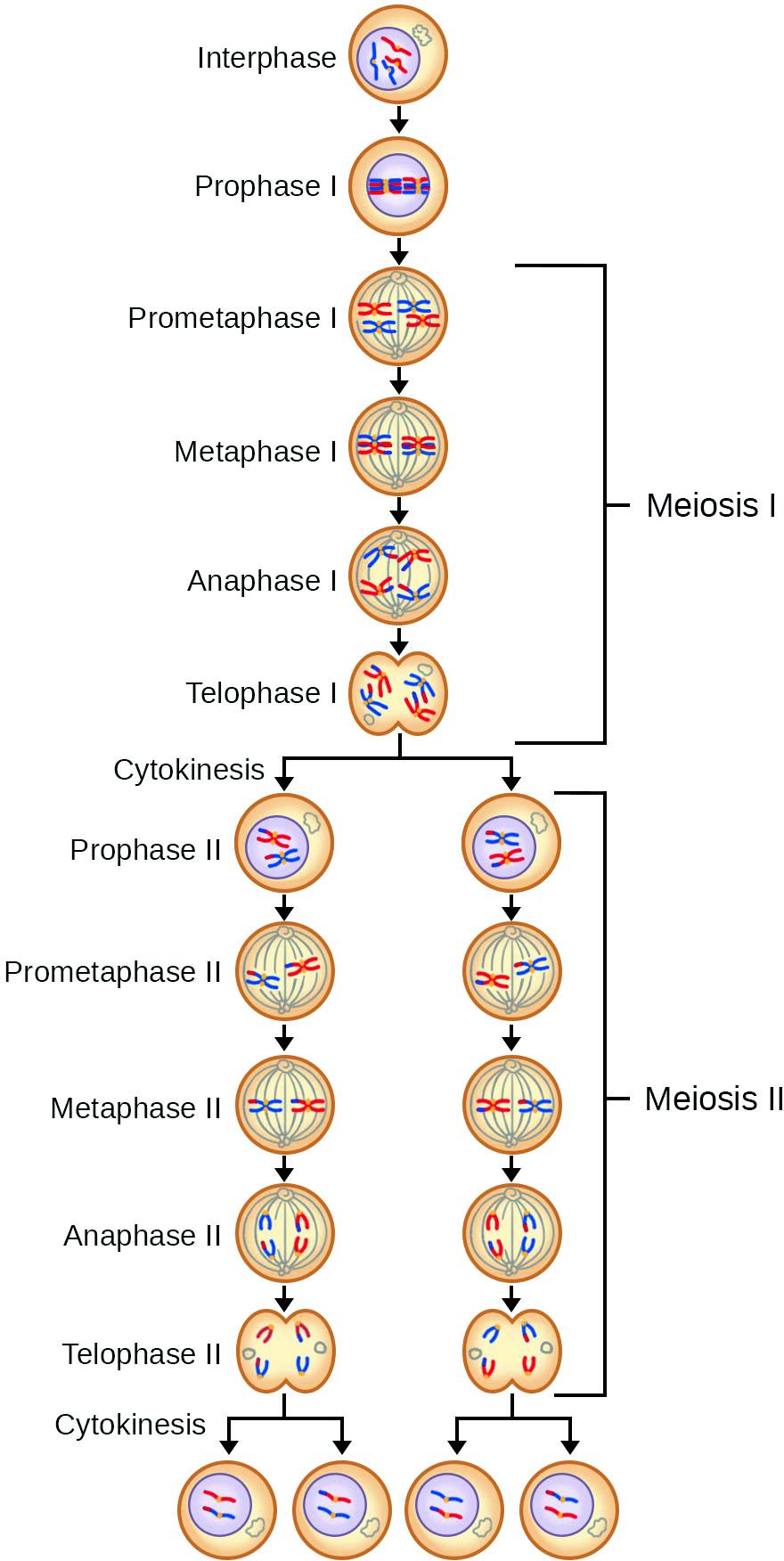
It starts right after Cytokinesis, even before the full elongation of the chromosomes. Prophase II is simpler than Prophase I to a great extent. Thus, anaphase II failed to occur and sister chromatids were not released. Prophase II is the first step in the process of Meiosis II. The centrosomes move towards the poles of the cell and spindle fibers form. Cells with scattered chromosomes were unable to progress in meiosis. During prophase II of meiosis, the chromosomes condense again and the nuclear envelope breaks down once more.

While in one cell the chromosomes were totally aligned at the metaphase II plate, in the other they could be found completely scattered, leading to an asynchronous cell division. During prophase I, they coil and turn shorter and thicker. The initial stages of prophase I am characterized by the duplication of the chromosomes. Prophase II is similar to mitotic prophase. The behavior of sister cells was inconsistent. Prophase I is the most complex stage of meiosis because in this phase, the homologous chromosomes should pair and the genetic information gets exchanged. Some chromosomes did not reach the metaphase II plate and remained scattered. However, in late prophase II, owing to the breakdown of the nuclear envelope, the chromosomes were scattered in the cytoplasm. Early prophase II was normal with the chromosome set enclosed by the nuclear envelope. In meiosis II, however, frequency of abnormalities increased exceptionally. Meiosis I had a low frequency of abnormalities, mainly related to the chiasma terminalization process. unlike before prophase I, there is no interphase before prophase II. The difference between prophase I and prophase II is that crossing over between chromosomes takes place only in prophase I, not on prophase II.Cytological characterization of BRA005568 accession of Brachiaria ruziziensis (2n = 2x = 18) showed a totally unexpected high frequency of abnormal meiotic products, from triads to hexads, and also tetrads with micro nuclei or microcytes. It is the beginning phase of another subsequent cell division after meiosis I. Prophase II ends where metaphase II begins. Spindle fibers grow outward from the centrosomes. The centrosomes replicate and move towards the opposite poles. If interkinesis takes place, the nuclear envelope and the nucleolus disintegrate during prophase II. Prophase II is the phase that follows after meiosis I, or after interkinesis if present. During the metaphase II, two spindles one from each pole attach with the centromere of each chromosome. Chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate individually. Furthermore, spindles develop from each pole. Each of these phases is designated as I or II depending where it occurs, i.e. During the prophase II, chromosomes condense and nuclear membranes break. These are prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Prophase II, the first step of meiosis II, begins with the two daughter cells produced by the first meiotic division (see figure right). That is because the parent cell undergoes two meiotic divisions called first meiotic division ( meiosis I) and second meiotic division ( meiosis II). The resulting cells following meiosis contain half of the number of the chromosomes in the parent cell. Meiosis is a reproductive cell division since it gives rise to gametes. The first stage in meiosis II highlighted by the disintegration of nucleolus and nuclear envelope, the shortening and thickening of the chromatids, and the replication and movement of centrosomes to polar regions


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
